Native pollinators are vital to the function of our ecosystem, but pollinator populations are declining in Iowa due to habitat loss, invasive species, pesticide misuse, and disease. To help prevent further decline, the University of Iowa has committed to protecting our native pollinator population by becoming a Bee Campus USA affiliate, an initiative of the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation.
The UI has a Bee Campus Committee which includes students, faculty, and staff from the UI. The committee is tasked with ensuring the UI meets its requirements to maintain Bee Campus USA affiliation. If you would like to join the Bee Campus Committee, please email sustainability@uiowa.edu.
Sustainability is an important priority for the university. Becoming a Bee Campus will provide us with a platform to demonstrate and communicate our commitment to addressing complex sustainability challenges.
Our Bee Campus Commitments
Habitat
We will create and enhance pollinator habitat by increasing the abundance of native plants and providing nest sites
Pesticides
We will embrace integrated pest management practices and minimize our use of pesticides
Education
We will provide our campus community with educational opportunities focused on pollinator conservation
Engagement
We will provide service-learning projects that enhance pollinator habitat

Pest Management
Campus Landscape Management
The University of Iowa campus comprises over 1,700 acres of diverse landscape which is managed by UI Landscape Services, Athletics Grounds Maintenance, and contracted vendors.
Integrated Pest Management
The university has imbedded Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices into its operations and requires external vendors to utilize IPM principles to control insect, disease, and weed pests.
Pests are populations of living organisms that pose a health or safety risk, damage property, or interfere with the aesthetics or use of facilities for human purposes. IPM establishes a sustainable approach to managing pests to an acceptable level by combining biological, cultural, physical and chemical tools. This in turn minimizes economic, health, and environmental risks of pests and pesticides.
IPM is a means to deliver effective pest control while at the same time reducing the volume and toxicity of pesticides used. However, in some circumstances, small amounts of organic and/or synthetic pesticides may be needed to maintain pest populations at or below an acceptable level. Decisions concerning whether pesticides should be applied in a given situation should be based on a review of all available options. Efforts should be made to avoid the use of pesticides by utilizing non-chemical IPM strategies. When it is determined that pesticides are warranted to meet pest management objectives, treatments should be undertaken carefully. Have the goal of controlling only target organisms to an acceptable level in specific areas. Use the least toxic product adequate for the job.
Additional Resources

Iowa's Native Plants
What is a Native Plant?
Native plants are species that occur naturally in the region in which they evolved. In North America, native species are generally recognized as those occurring on the continent prior to European settlement. Find more information here.
What Plants are Native to Iowa?
Below are resources to help you find plants that are native to Iowa. Keep in mind, plants considered native to Iowa may be found across the entire state, or they may be found only in specific parts of the state. Just because something is identified as an Iowa native, does not mean it is native to the entire state.
Where Can I Get Iowa Native Plants?
Below are resources to help you find nurseries or retailers that offer native plants. We do not endorse any particular vendors and are simply providing resources we are aware of.
Bee Campus News
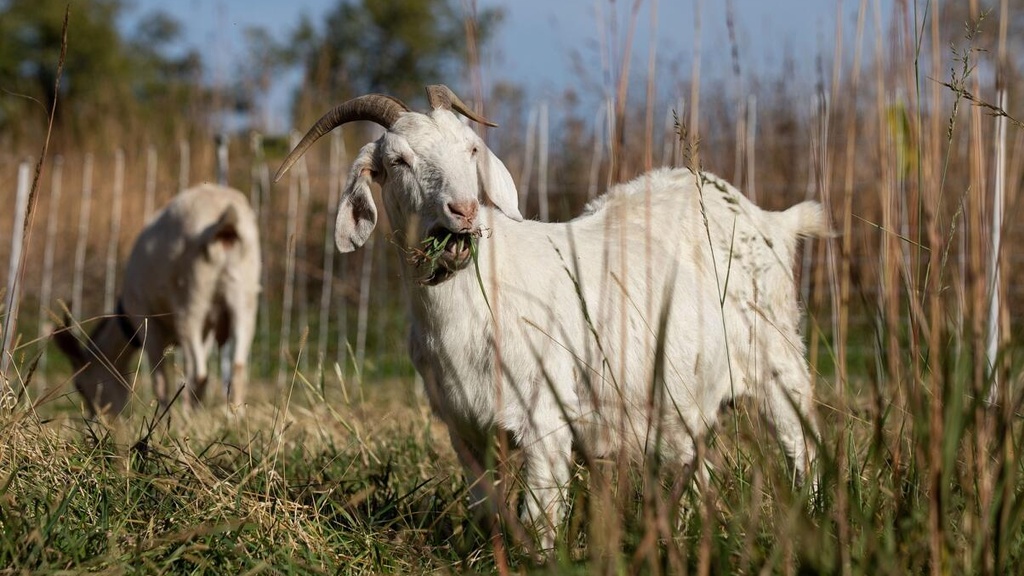


Go-At It Land Stewardship Provides New Goatscaping Option for Eastern Iowa